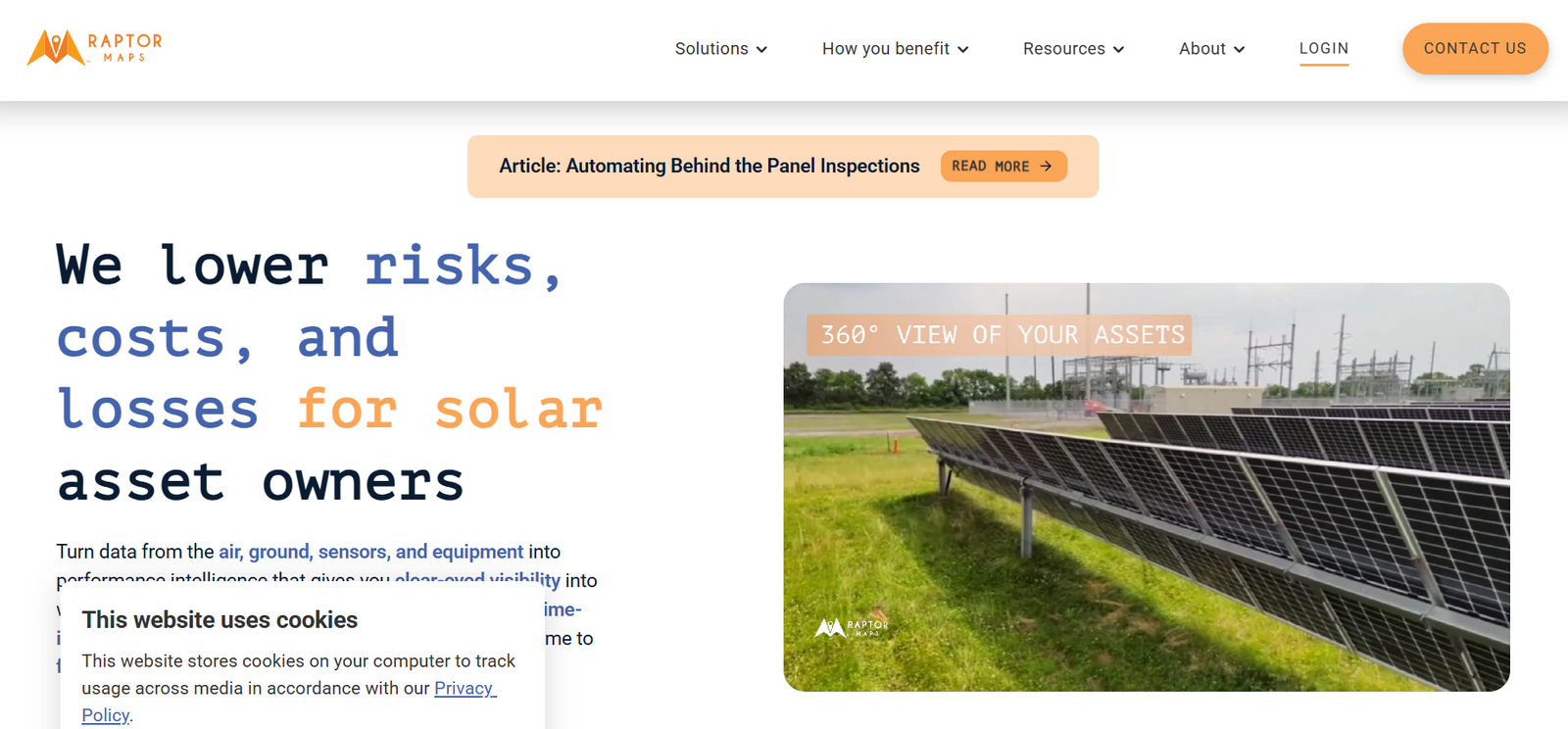
Raptor Maps is a solar asset management software platform that empowers solar companies to optimize the performance, maintenance, and profitability of their photovoltaic (PV) assets. Founded in 2015 by MIT engineers, Raptor Maps uses a combination of drone data, machine learning, and digital asset modeling to improve the efficiency of solar operations across utility-scale, commercial, and industrial solar projects.
The platform serves as a central hub for managing the entire lifecycle of a solar asset—from aerial inspections and maintenance tracking to performance analysis and warranty claims. With solar power becoming a critical component of global energy infrastructure, Raptor Maps provides the tools asset owners, operators, and EPCs need to scale operations and reduce manual labor.
Raptor Maps is widely adopted by solar developers, O&M providers, asset managers, and independent engineers. The company’s software processes data from aerial inspections and converts it into actionable insights that can drive up energy yield and reduce operational costs.
Features
Raptor Maps offers a suite of robust features specifically designed to streamline solar asset management and enhance energy production.
One of its core features is aerial thermography inspection processing. The platform analyzes drone or aircraft-captured thermal and RGB imagery to identify faults such as hotspots, disconnected modules, or inverter issues. This helps asset managers prioritize maintenance and reduce downtime.
The Raptor Solar™ platform, the company’s flagship product, supports digital twins of solar assets, which serve as accurate, up-to-date representations of each site. These digital models include electrical diagrams, layout maps, component metadata, and historical inspection data—all accessible in one place.
Raptor Maps also provides automated anomaly detection using machine learning algorithms. This feature significantly cuts down on the time needed to review imagery, offering consistent, unbiased results across all assets.
The software includes work order management tools that allow users to assign, track, and verify maintenance tasks. These tools integrate with inspection reports so that faults identified during aerial scans are automatically translated into actionable tasks.
Another feature is performance analytics, which help identify underperforming sections of the solar array. Users can correlate inspection data with energy production figures, financial loss estimates, and warranty eligibility.
The platform is also hardware agnostic, meaning it supports data input from various drones, sensors, and cameras. Users can upload data collected from DJI drones or manned aircraft using standard industry formats.
How It Works
Raptor Maps starts with the collection of high-resolution thermal and RGB images of solar sites using drones or aircraft. These images are then uploaded to the platform, where Raptor Maps’ proprietary machine learning algorithms process them to detect and classify anomalies.
Once the imagery is processed, users are provided with a comprehensive report that includes GPS-located faults, estimated power loss, severity classification, and visual overlays. These reports are accessible through the Raptor Solar™ interface, which acts as a centralized dashboard for all site data.
From there, users can review flagged issues, generate work orders, and track maintenance actions directly in the platform. The software allows users to overlay inspection data with layout schematics, inverter strings, and other metadata, providing context that improves troubleshooting accuracy.
The digital twin updates automatically as new inspection data is added, and users can filter anomalies by type, location, or severity. Integrations with SCADA systems and other solar monitoring platforms enable seamless data sharing and system-wide analysis.
Use Cases
Raptor Maps is used across the solar energy value chain by various stakeholders looking to improve operational efficiency and financial performance.
Solar asset owners and independent power producers (IPPs) use the platform to gain full visibility into asset performance and to verify that their portfolios are meeting expected returns. The platform supports performance benchmarking and investor reporting.
Operations and maintenance (O&M) providers benefit from Raptor Maps’ work order management and automated fault detection. This leads to faster repair cycles and lower operational costs.
Engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) companies use Raptor Maps for post-construction inspections and commissioning, ensuring that systems are installed correctly and functioning as intended.
Independent engineers and insurance providers utilize the platform’s inspection reports to validate system health, assess warranty claims, and determine asset value during transactions or audits.
Developers and analysts use the historical performance data and inspection analytics to plan expansions, repowering efforts, and optimize asset lifecycles.
Pricing
Raptor Maps offers custom pricing based on the size and complexity of the solar portfolio. There are no flat-rate or public pricing tiers listed on the official website.
Pricing typically depends on factors such as:
Total megawatts (MW) of the solar asset
Number of inspections per year
Use of advanced analytics and integrations
Access to the Raptor Solar™ digital twin system
Level of support and training required
Interested parties can request a demo or contact the Raptor Maps sales team via the website to receive a tailored quote. The company also offers pilot programs and scalability options for large enterprises.
Strengths
Raptor Maps stands out for its industry-specific focus on solar energy, offering tools that are purpose-built for photovoltaic systems rather than general asset management.
Its ability to process aerial imagery using machine learning significantly reduces manual labor and delivers high-accuracy results. The digital twin feature adds a powerful layer of context, making it easier for teams to locate, track, and resolve issues.
The platform’s hardware-agnostic design ensures compatibility with a wide range of drones and sensors, giving users flexibility in their operations. Additionally, its cloud-based dashboard allows for centralized data management and remote collaboration across global teams.
The inclusion of power loss estimation and ROI analysis helps stakeholders link physical faults to financial outcomes, supporting smarter decision-making.
Drawbacks
One limitation of Raptor Maps is the lack of transparent pricing on the website, which can make initial evaluation difficult for smaller firms or new market entrants.
Another drawback is the requirement for drone or aircraft data collection, which may be a barrier for companies that lack access to aerial imaging hardware or skilled pilots. While Raptor Maps offers guidance, data acquisition remains a critical responsibility for the user.
The platform is specialized for solar applications, meaning it is not suitable for managing other types of energy assets like wind or hydro. This limits its applicability to broader renewable portfolios.
Comparison with Other Tools
Compared to general asset management software like UpKeep or Asset Panda, Raptor Maps is much more specialized and targeted for the solar industry. These general tools lack features like thermal anomaly detection, digital twins, and integration with drone inspection data.
When compared with solar-focused competitors like DroneDeploy or Scopito, Raptor Maps offers deeper analytics, better fault classification, and a more robust reporting system tailored to PV systems. While DroneDeploy excels in mapping and site visualization, Raptor Maps leads in actionable analytics and solar-specific insights.
Another similar platform, SenseHawk, offers digital tools for solar site operations, but Raptor Maps is often favored for its scalability, global support, and deeper fault diagnostics based on thermography.
Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Raptor Maps has been praised by users for its accuracy, ease of use, and significant time savings. According to customer testimonials on the official website, clients have reported a 95% reduction in inspection analysis time and improved ROI through faster maintenance cycles.
Companies like AES, SolarSense, and Nexamp have cited Raptor Maps as a key partner in their solar asset operations. Users appreciate the platform’s intuitive interface, fast processing times, and ability to convert raw imagery into reliable insights.
Though Raptor Maps is not listed on popular software review platforms like G2 or Capterra, its reputation within the solar industry is strong, especially among O&M providers and IPPs managing multi-MW portfolios.
Conclusion
Raptor Maps is a specialized, high-performance platform that brings automation, analytics, and scalability to the solar asset management industry. By transforming aerial inspection data into actionable insights, it helps asset owners and operators maximize uptime, improve efficiency, and increase the profitability of their solar investments.
The combination of thermal imaging analysis, digital twins, and work order tools makes Raptor Maps an all-in-one solution for modern solar operations. Though the platform is geared toward large-scale commercial and utility solar projects, its scalable pricing and hardware compatibility make it accessible to a broad range of users in the solar value chain.